Have you heard of insulin resistance but are not sure what it is? Are you gaining weight no matter what you do or have been diagnosed with diabetes or pre-diabetes? This article will explain exactly what insulin resistance is and the best way to support normal blood sugar.

All of this information came from my Keto & Intermittent Fasting Coaching Course from Dr.Berg. This is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified healthcare provider.
What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas. It transfers sugar from the blood to the cells, so is therefore used to lower your blood sugar whenever you eat. Sugar and carbs spike blood sugar more than anything else.
Every time your blood sugars rise after eating a meal or snack, insulin is required to bring the blood sugar down. It moves the sugar (or glucose) from the blood to the cells.
What is insulin resistance?
The body doesn’t like receiving very much insulin at a time. So eating foods high in sugar and carbs creates high insulin.
Insulin resistance happens is when you have high insulin in the body for too long of a period of time, then the cells begin resisting it, saying “I don’t want any more of this, I’m going to start rejecting it!”
The cells start to reject the insulin because too much can be toxic, so this is actually a protective mechanism in your body.
Then this process signals the pancreas to produce more insulin because the cells aren't receiving what they need, and this creates a never-ending loop effect.
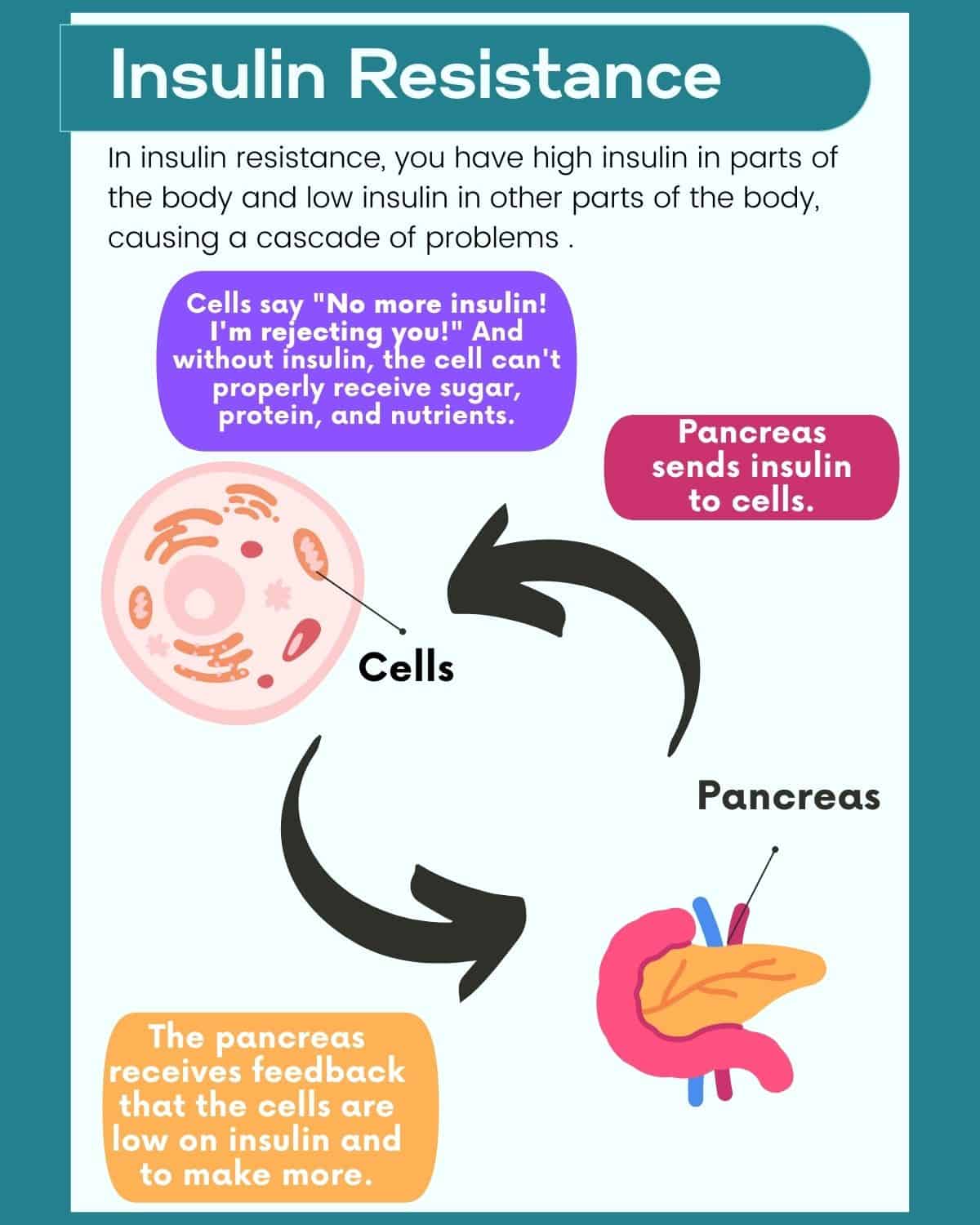
When your cells stop accepting the insulin, sugar accumulates in the blood and you get HIGH BLOOD SUGAR.
In effect, insulin resistance is the cause of type-two diabetes.
Some symptoms of high blood sugar include:
Short Term:
- increased thirst
- sleepy after meals
- frequent urination
- sleepy
- weakness
- trouble concentration
- high blood pressure
- tingling
- ear infections
- restlessness
- inflammation
- frequent hunger
- dry mouth
- dry skin and more
Long Term:
- neuropathy (due to nerve damage)
- eye damage (dry eyes, macular degeneration, floaters, blindness, glucoma, cataracts, etc..)
- brain problems (memory issues & brain shrinkage)
- kidney problems
- heart issues (plaquing in arteries, clots causing heart attacks and strokes)
- belly fat
- itching
- fatty liver and more
In addition to sugar (or glucose), the nutrition, minerals, and protein also aren't entering the cells correctly.
Because of this, people have poor muscle tone and nutrient deficiencies since they aren't absorbing what they eat.
This is also why people with insulin resistance don't usually feel satisfied after eating. They typically crave something sweet after a meal to stimulate more insulin to get the nutrients into the cells.
Surprisingly, people with type 1 diabetes can also have insulin resistance! If high levels of insulin injections are required, the cells can still become resistant, requiring more and more insulin to bring blood sugars within the normal range.
One odd thing is we often have high insulin in one area of the body and low insulin in another, yielding symptoms of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia at the same time.
For an in-depth video on this, be sure to watch my Patreon video, Why Keto + Understanding Insulin!

In the video, I answer the following questions:
- Are all carbs bad?
- Are whole grains healthy?
- What's the real reason I'm so addicted to carbs?
- What's wrong with carbs?
- What are the symptoms of insulin resistance?
- Why can some people eat carbs without gaining weight?
- Is keto healthy and does it work?
- How is insulin related to keto?
- And so much more!
Symptoms of insulin resistance
A person can have normal blood sugar, despite having symptoms, with insulin resistance for years (even decades!) before the blood sugar starts going up or it shows up as pre-diabetes or diabetes.
Why? Because your body is doing its best to regulate itself and keeps pumping out more and more insulin to keep blood sugars down.
After a certain point though, your cells will no longer respond to insulin, causing your blood sugar to go up.
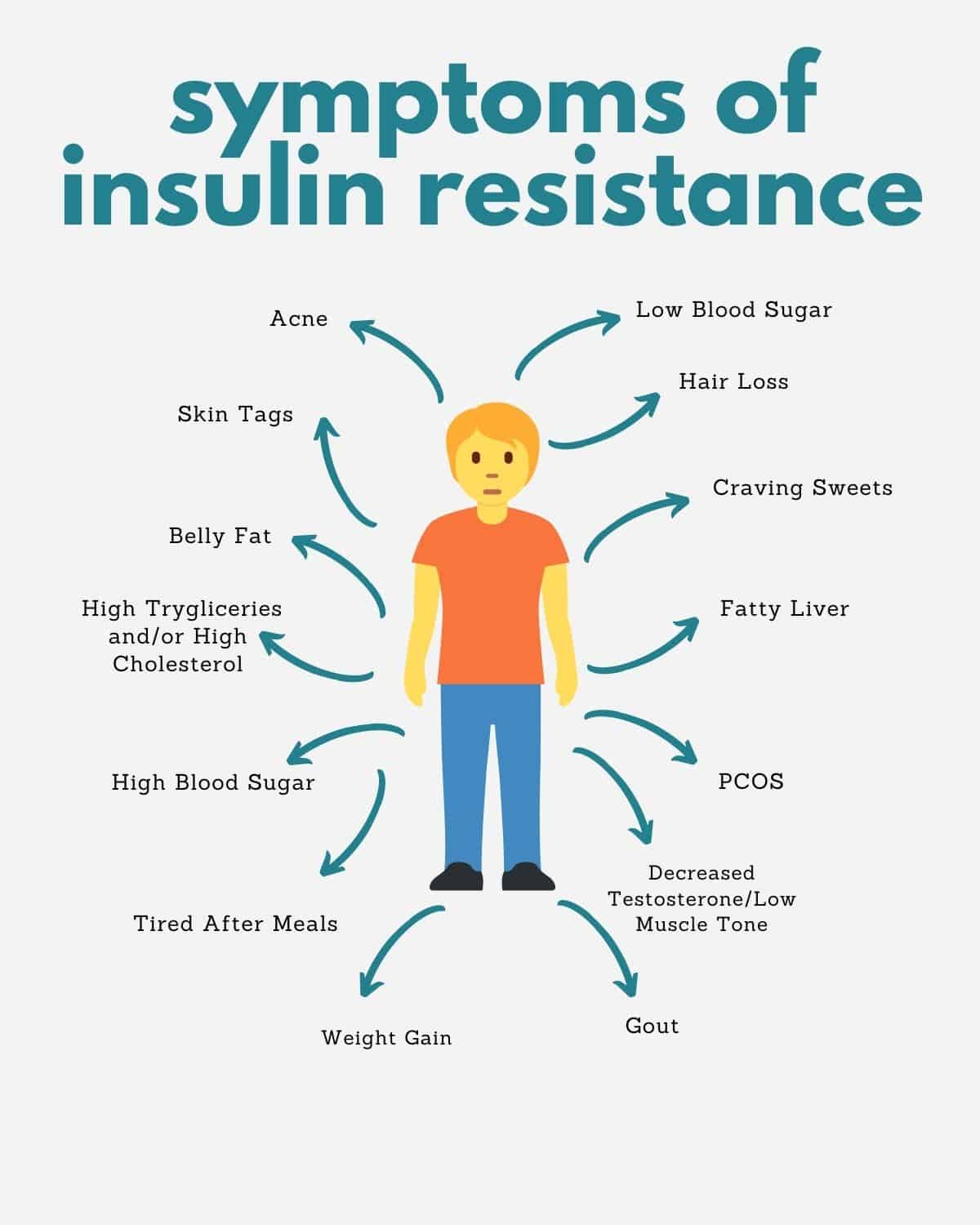
Here are some symptoms of insulin resistance:
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar, sometimes happens before high blood sugar sets in. Includes: insomnia, itching, frequent sighing or yawning, tinnitus, cravings, headaches, anxiety, heart palpitations, cold extremeites, fatigue, fainting, shaking, increased heart rate, and more)
- Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar, talked about above👆)
- Belly Fat
- Fatty liver
- Hunger
- Not satisfied after eating
- Loss of muscle tone
- Craving for sweets
- Acne
- PCOS
- Hair loss
- Skin tags
- Gout (increased uric acid)
- Low potassium
- High sodium
- Dark patches (back of neck, groin and arm pit)
- High Triglycerides
- High Cholesterol
- Inflammation
- Tired after meals
- Plateaued weight or weight gain
- High insulin (talked about below👇)
- Deceased testosterone
Effects of high insulin
Besides lowering blood sugar, insulin also turns excess sugar into fat, especially belly fat.
As you start developing high insulin (called hyperinsulinemia), the insulin starts storing fat in the fat cells until the cells are completely full.
At some point, the cells just can't take any more fat and it starts storing fat in the liver, causing a fatty liver. After the liver and fat cells, it starts storing fat around the organs, arteries, and all over the place!
And as mentioned earlier, high insulin can wreak havoc on your body for years (including weight gain, insulin resistance, and more!) until it starts showing up as high blood sugar!

High insulin is a surprising root cause of many major symptoms, diseases, and disorders including:
Short Term:
Long Term:
- High blood pressure
- Sodium retention
- High cholesterol
- High triglycerides
- Muscle weakness
- Brain fog
- PCOS (increases androgens)
- Decreased concentration
- Vision loss
- Weight gain
- Increases inflammation
- Increases stiffness
- Atherosclerosis (heart attack)
- Diabetes
- Thickened arteries (HBP)
- Blood clots (Stroke)
- Cancer
- Calcified arteries
- Alzheimer’s (amyloid plaquing)
- Stroke
- Dementia
- Early risk of death
Basically, all our major diseases come from high insulin! As soon as people begin to lower their insulin, they start becoming healthier and losing weight.
How To Support Normal Blood Sugar
Normal blood sugar and insulin levels are best supported by following a healthy keto diet along with intermittent fasting.
By following a keto diet, you can reduce the amount of insulin needed to bring your blood sugar down and the overall amount released in your body.
However, every time you eat you trigger insulin, at least to some degree. This is why I also recommend intermittent fasting.
Fasting allows your body time to 'clean house', lose weight, and treat insulin resistance.
If you are new to intermittent fasting, the best way to start is simply by cutting out snacks! I recommend eating 3 meals a day with NO SNACKING for at least 3 weeks.
After that, you can experiment with trying to go longer without eating, eventually going down to 2 meals a day, if possible.
When fasting, be sure to 1) eat enough fat to keep you full until the next meal. It will keep you satisfied and won't spike insulin. And 2) keep your carbs low. Too many carbs will spike insulin, make you hungrier, and will slow your metabolism.
Here are some more things that will help support healthy blood sugar and insulin levels:
- Apple cider vinegar lowers insulin. Add 1 teaspoon per glass of water or use on salads.
- Fermented foods from pickles to kim chi. Any fermented vegetables help lower insulin and improve gut health.
- Getting enough potassium (you need a whopping 4700mg a day!) with lots of veggies. I recommend 7-10 cups of veggies a day to get all your nutrients - it sounds more daunting than it is.
- Getting enough B1 in the diet (nutritional yeast is the best source).
- More fiber helps with insulin resistance, and celery is good for this.
- Magnesium (found in nuts, seeds, avocados, & dark leafy greens).
- Vitamin D (found in cod liver oil or the sun).
- Sleeping more.
- Exercise.
- Chromium.
Summary
Insulin is your fat-storing hormone and can cause all kinds of symptoms, diseases, and disorders when it is too high.
You can have high insulin with symptoms for years before it shows up as high blood sugar. This is because your body is doing its best to regulate itself and keeps pumping out more and more insulin to keep blood sugars down.
After a certain point, your cells will no longer respond to insulin, becoming insulin resistant. In turn, this causes more to be produced, creating a terrible loop.
When the insulin receptors in your cells stop accepting the insulin, sugar accumulates in the blood and you get HIGH BLOOD SUGAR.
Insulin resistance is the cause of type 2 diabetes and is best supported by following a healthy keto diet with intermittent fasting. Apple cider vinegar, potassium, magnesium, lots of veggies, and B-vitamins (among other things) will also help.






Comments
No Comments